The siena microsimulation model (SM2) for net-gross conversion of EU-silc income variables
- Article
- Figures and data
- Jump to
Figures
Tables
Gross-to-Net conversion algorithm.
| Income measure | Total | By component a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GROSS b | G=ΣGi ← | Gi |
| 2 | Social Insurance contribution | Si = Si(Gi) | |
| 3 | GROSS TAXABLE | H=ΣHi ← | Hi = Gi − Si |
| 4 | Component-specific deductions | Di = Di(Hi) | |
| Aggregation over components and individuals in tax unit | |||
| 5 | TAXABLE INCOME | Y=Σyi ← | Yi = Hi − Di |
| 6 | Common deductions | D0 = D0(H) | |
| 7 | Taxable income (after deduction) | Y0 = Y − D0 | |
| 8 | Tax due (before credits) | W0 = W0(Y0) | |
| 9 | Common tax credits | C0 = C0(Y0) | |
| 10 | TAX DUE | W = W0 − C0 | |
| 11 | Component-specific tax credits | C = ΣCi ← | Ci = Ci(Yi) |
| 12 | TAX PAID | X = W − C | |
| 13 | TOTAL NET INCOME | N = H − X | |
| 14 | Tax rate (descriptive) | R0 = X/H | |
| 15 | TAX RATE = TAX DUE/ TAXABLE INCOME | R = W/Y | |
| Disaggregation – personal income by component | |||
| 16 | Proportionate tax by component | Xi = (R*Yi) – Ci | |
| 17 | NET INCOME BY COMPONENT | Ni = Hi – Xi | |
-
a
The functional relationships in this column may be somewhat more complex or varied.
-
b
Gross including employers’ social insurance contribution (SS) is: GG = G + SS(G1)
Forms of reporting of an income component.
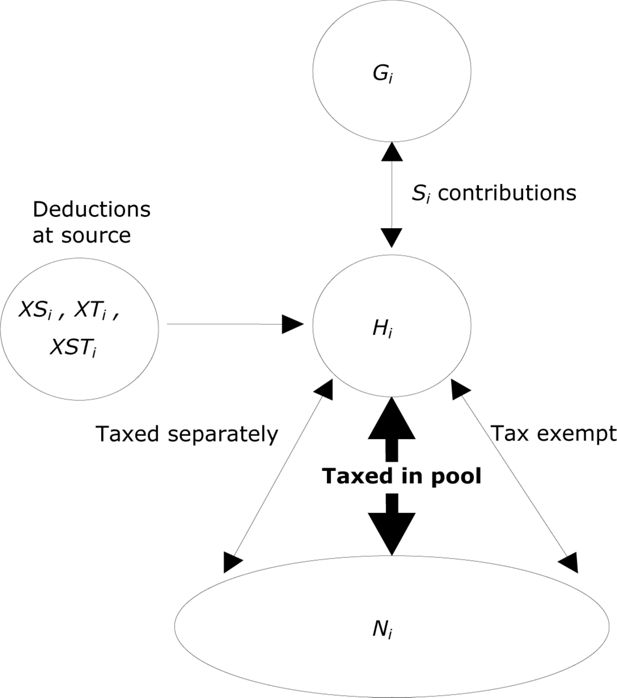
| Income component (i) subject to tax and social insurance contributions | |
| Form (Xi) in which data on the income component have been collected: | |
| Gi | gross income (before tax and social insurance contributions, if applicable) |
| Hi | gross taxable (before tax, but after social insurance contributions, if any) |
| Ni | net income (after deducing ‘final’ tax and social insurance contributions, i.e., as the final amount actually received) |
| Income received after retentions at source: | |
| XTi | taxed at source (but no social insurance contribution); Ti = tax at source |
| XSi | Social insurance contributions (but not tax) at source; Si = social insurance contributions at source |
| XTSi | both tax and social insurance contributions at source; Ti + Si |
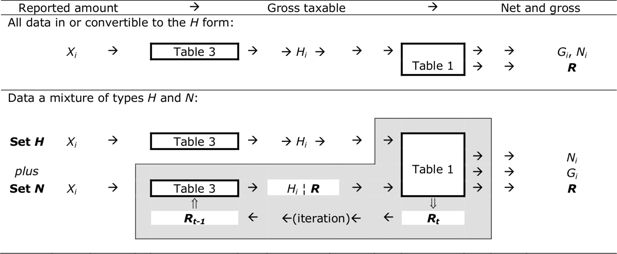
Calculation of Hi according to the form in which the component is specified.
| Set H | |||
| given value Pi = | XSi | Hi = XSi | Simple iteration, generally separately for each component |
| Gi | Hi = Gi − Si(Gi) | ||
| XTi | Hi = Gi − Si(Gi) where Gi = XTi + Ti(Hi) | ||
| XTSi | Hi = XTSi + Ti(Hi) | ||
| Set N | |||
| given value Pi = | Ni | Hi = Yi + Di(Hi) where Yi = [Hi − Ni + Ci(Yi)] / R |
Double iteration (i) with assumed R, for each component in turn (ii) for determining R, common to all pooled components |
-
Set N: set of income components which are subject to income tax (irrespective of whether the component is also subject to social insurance contributions), and for which the ‘final net’ amount (Xi = Ni) has been specified in the data collected.
-
Set H: all other income component (not subject to tax, or for which the data has been collected in a form other than
Examples of special deductions and tax credits.
| Form of taxation of component i | Special deduction | Special tax credit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tax exempt | Di = Hi | − |
| 2 | Taxed at flat rate fi | Di = Hi | Ci = −fi × Hi |
| 3 | Tax-exempt at flat rate fi | − | Ci = +fi × Hi |
| 4 | Deductions for expenses | + common deductions | − |
| 5 | Tax credit for expenses | − | + common tax credits |
| 6 | Special tax not related to income | − | − common tax credits |
| 7 | Double taxation at flat rate fi | − | Ci = −fi × Hi |
| 8 | Part ΔSi of social insurance contributions subject to tax | −ΔSi | − |
-
Different forms may apply to cases like 3, 4 and 7: for instance the tax rate being a more general function of the amount of income involved for the component concerned.
Main components of income, and tax and social insurance deductions in the Italian fiscal system (year 2003).
| N | Income Components | Social Insurance Contributions (Si) | Tax | Included in common pool | Component-specific | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deduction (Di) | Tax Credits (Ci)c | |||||
| 1 | Employment income | Employer’s S0(G1) Employer’s S0(G1) |
IRPEF a | X | D1(Y1) | |
| 2 | Self-employment income | S2(G2) | IRPEF | X | D2(Y2) | −f2(H2) IRAP d |
| 3 | Pensions | IRPEF | X | D3(Y3) | ||
| 4 | Non-financial capital income | IRPEF | X | |||
| 5 | Property (rental and cadastral) income | IRPEF c | X | |||
| 6 | Financial Capital income | Taxed at source (flat rate K6) | H6 | −K6 × H6 | ||
| Education related benefits, Unemployment benefits | IRPEF | X | ||||
| 7 | Family benefits, Sickness invalidity benefits d, Housing allowances, Any other personal benefits. | Tax exempt | H7 | |||
| Assets | ||||||
| 8 | Property value | ICI (on value of real estate) | −f8(value) | |||
-
a
Above a certain limit and if it not taxed at source
-
b
Additional tax on self-employment income (IRAP, Tax on income from production activities). f(..) stands for "a function of"
-
c
On total cadastral and on 85% of the rental income
-
d
Part of the benefits may be taxable
EU-SILC target variables: distribution of income by component.
| Ratio net/gross | ||
|---|---|---|
| 6.1.1.1.1.1 | Income from work | 64.5 |
| PY010 | employee cash or near cash income | 85.9 |
| employer’s SI contribution | ||
| employee’s SI contribution | ||
| PY050 | cash benefits or losses from self-employment | 76.3 |
| Self-employed SI contribution | ||
| 6.1.1.1.1.2 | Property income | 80.7 |
| HY090 | interest, dividends, profit from capital investments in unincorporated business | 81.1 |
| HY040 | income from rental of a property or land | 80.2 |
| 6.1.1.1.1.3 | Taxable benefits | 88.6 |
| PY090 | unemployment benefits | 92.5 |
| PY100 | old-age benefits | 88.7 |
| PY110 | survivor’ benefits | 87.9 |
| PY130 | disability benefits | 90.2 |
| 6.1.1.1.1.4 | Tax-exempt social transfers | 100.0 |
| PY140 | education-related allowances | 100.0 |
| HY050 | family related allowances | 100.0 |
| HY060 | social assistance | 100.0 |
| HY070 | housing allowances | 100.0 |
| HY080 | regular inter-household cash transfer received | 100.0 |
| Total | 71.3 |
Comparison with external sources: distribution of total gross income.
| SM2 | ISTAT | Error (% point) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gross including SI | 100.0 | 100.0 | |
| SI contributions | 15.9 | 15.7 | 0.2 |
| − Employers’ contribution | 9.9 | 11.4 | −1.5 |
| − Employees’ contribution | 3.5 | 2.8 | 0.7 |
| − Self -employment contribution | 2.5 | 1.6 | 0.9 |
| Gross taxable | 84.1 | 84.3 | −0.2 |
| Personal income tax and financial tax | 12.8 | 12.0 | 0.8 |
| Net income | 71.3 | 72.2 | −0.9 |
-
Sources: ISTAT: National Accounts (2003); SM2: Model run using Italy EU SILC Wave 1 (2003) as input
Main components of income, and tax and social insurance deductions: Spain (year 2003)
| Income component | ECHP/SILC variable | Social insurance contribution | Taxed at source | Tax-exempt | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Employees’ income | (PI1111/PY010), regular wage/salary earnings excluding lump-sum | Employers’ contribution f ; Employees contribution; Unemployment. Insurance. g | X a | |
| 2 | Unemployment benefits | (PI131/PY090) | X a | ||
| 3 | Pensions | (PI132/PY100 + PY110) includes old age and survivor’s benefits (2 EU-SILC variables) | X a | ||
| 4 | Family related benefits | (PI133/HY050) | X a | ||
| 5 | Sickness invalidity benefits | (PI134/PY120 + PY130) (2 EU-SILC variables) | X a | X b | |
| 6 | Other taxable personal benefits | (PI136/PY150) | X a | ||
| Flat rate taxed withholding | |||||
| 7 | Employees’ lump-sum income | (PI1112) | X c | ||
| 8 | Self-employment income | (PI112/PY050) | Self-employed social insurance | X d | |
| 9 | Capital income | includes both financial and non-financial capital income (PI121/HY090) | X d,e | ||
| 10 | income from renting out buildings or land | (PI122/HY040) | X d,e | ||
| Tax exempt | |||||
| 11 | Education related benefits | (PI135/PY140) | X | ||
| 12 | Housing benefits | (HI138/HY070) | X | ||
| 13 | Social assistance | (HI137/HY060) | X | ||
| 14 | Private transfer received | (PI123/HY080) | X | ||
-
a
All these components are taxed at source following the same rules as applied to employment income. The tax rate for deduction at source is determined on the basis of incomes from components 1–6, taken one at a time. By contrast, the final tax rate (IRPF) is determined on the basis of pooled income from all taxable components 1–10.
-
b
Some benefits in these categories are tax exempt, e.g. when the individual is completely disabled, or receive sickness benefit due to HIV
-
c
Taxed at source at the same rate as determined on the basis of (and applied to) employee’s income.
-
d
Taxed at source at a fixed (flat) rate, depending on the component concerned.
-
e
Certain (in particular non-financial) forms of capital income are not subject to withholding at source. Also special or local withholding rates apply to some forms. Similarly, only a part of rental income is subject to withholding. Assumption in the application using available data: As it was not possible to distinguish between different forms of capital income, in our application to ECHP data all capital income was treated in a uniform way as financial capital income.
-
f
Employee’s ‘gross income’ (including tax and social insurance contributions of the employee), plus employer’s social insurance contribution gives ‘labour cost’.
-
g
Assumption in the application using available data: It was assumed that unemployment insurance contributions are made by all employees, but only during the time they are in employment. In reality, not all persons in employment may make this contribution because it is not obligatory. On the other hand, persons may continue to make this contribution also during any periods of unemployment. Such variations are not available in data such as ECHP at the micro-level.
Main components of income, and tax and social insurance deductions: France (year 2003)
| Income from employment | |
| Total Cost of Labour | GG1 |
| Gross wages | G1 = GG1 − S0 |
| Wages Net of Social Insurance Contributions | H1 = G1 − S1 |
| Income net of social contributions | |
| Net Income | H − H8 a |
| Total Net Income | H |
| Tax base and tax | |
| Revenus Catégoriels | Yg = (H − Hs) + ΔS |
| Revenus Catégoriels Net | Yn = Yg − (D1 + D2 + D3 + D4) |
| Taxable Income | Y = Yn − (D5 + D6 + D7 + D0)b |
| (basis for Quotient Familial and Income Taxation) | |
| Quotient Familial | Q |
| Net Income taxes (IR) | X = Q × W(Y/Q) − (C + C0) |
| Income after tax | N′ = H − X |
| Disposable Income | N = N′ + H8 |
| Constructing the income components in SM2 | |
| Gross income (including employers’ SI contributions) | GG = G + S8 |
| Employers’ social insurance contributions | S8 |
| Gross income (excluding employers’ SI contributions) | Gi; G = ΣGi |
| Income component (i) | |
| 1. Employment income | |
| 2. Self-employment income | |
| 3. Pensions | |
| 4. Unemployment benefits | |
| 5. Invalidity benefits | |
| 6. Capital income ‘A’; Capital income ‘B’ (in fact all capital income treated as ‘A’) | |
| 7. Other incomes: including property and rental income | |
| 8. Benefits ‘A’; Benefits ‘B’ (in fact all benefits treated as ‘B’) | |
| Social insurance contributions (other than employers’) | Si; taxable part ΔSi |
| Gross taxable income | Hi = Gi − Si; H = ΣHi |
| Component-specific deductions | Di; D = ΣDi |
| Net taxable income | Yi = Hi − (Di − ΔSi) ; Y = ΣYi = H − D |
| Common deductions | D0; Y0 = Y − D0 |
| Common tax credits | C0 |
| Quotient Familial | Q |
| Tax due | W = Q × W0(Y0/Q) − C0 |
| Component-specific tax credits | Ci; C = ΣCi |
| Tax to be paid | X = W − C |
| Total net income | N = H − X |
| Net by component | Ni = Hi − [{Yi (W/Y)} − Ci] |
-
a
H8 are tax and social insurance (SI) exempt benefits; hence H8 = N8
-
b
D5 to D7 are in fact zero (no component-specific deductions)