
Towards a European union child basic income?: Within and between country effects
- Article
- Figures and data
- Jump to
Figures

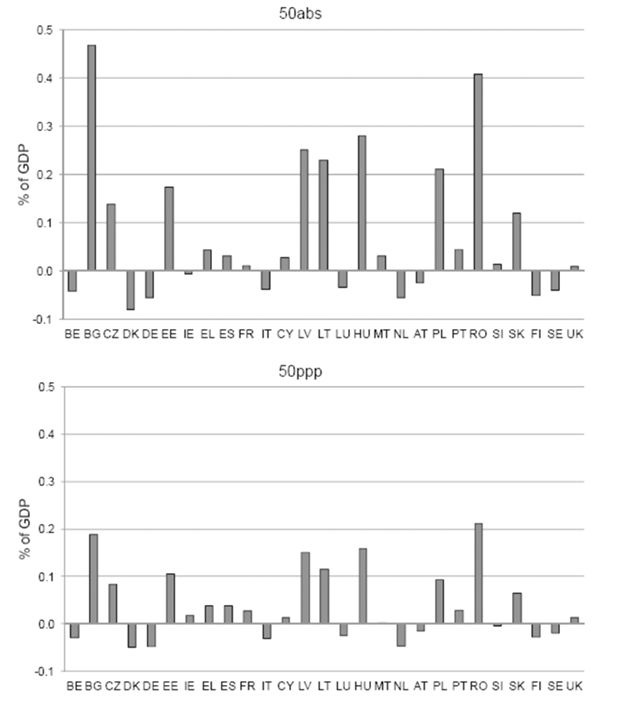
Cost and funding implications by country.
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes. As % of national GDP.
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.
Net flows as a percentage of national GDP.
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes.
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.

Net average benefit per child by income quartile group in euro per month.
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes. Euro per child per month. Average benefit is net of national and EU taxes; q1 = poorest 25%; q4 = the richest 25% of the distribution of equivalised household disposable income (for children aged under 6 only).
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.
Tables
Child Basic Incomes: target populations and benefit amounts.
| Share of children aged below 6 in the population (2010) (%) | PPP-adjusted €50 EU CBI (€ per month per child) | |
|---|---|---|
| Belgium | 6.9 | 55.70 |
| Bulgaria | 5.8 | 25.40 |
| Czech Republic | 6.3 | 37.60 |
| Denmark | 7.1 | 71.15 |
| Germany | 5.0 | 52.15 |
| Estonia | 6.7 | 37.40 |
| Ireland | 9.3 | 59.55 |
| Greece | 6.0 | 47.55 |
| Spain | 6.4 | 48.50 |
| France | 7.4 | 55.40 |
| Italy | 5.7 | 51.75 |
| Cyprus | 6.7 | 44.55 |
| Latvia | 6.0 | 36.10 |
| Lithuania | 5.8 | 32.55 |
| Luxembourg | 6.9 | 60.25 |
| Hungary | 5.8 | 32.45 |
| Malta | 5.8 | 38.95 |
| Netherlands | 6.7 | 53.80 |
| Austria | 5.7 | 53.10 |
| Poland | 6.0 | 30.95 |
| Portugal | 5.9 | 44.10 |
| Romania | 6.1 | 29.40 |
| Slovenia | 5.9 | 42.30 |
| Slovakia | 6.1 | 35.80 |
| Finland | 6.7 | 61.75 |
| Sweden | 7.0 | 60.80 |
| United Kingdom | 7.3 | 50.10 |
-
Notes: “PPP-adjusted €50 EU CBI” is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month, adjusted for power purchasing parity, to all children below the age of 6 in the EU.
-
Sources: Own calculations based on Eurostat (2012) Purchasing power parities, http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/purchasing_power_parities/data/database, Population by age in 2010: http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/population/data/database. Downloaded on 10 Feb 2012 15:45:33 MET.
Funding implications at EU level.
| EU CBI scheme | ||
|---|---|---|
| 50abs | 50ppp | |
| gross cost (million euro per year) | 18,302 | 17,928 |
| as % of EU budget | 12.98% | 12.72% |
| as % of EU GDP | 0.15% | 0.15% |
| national tax levied (million euro per year) | 2,740 | 2,760 |
| as % of gross cost | 14.97% | 15.39% |
| EU tax required (million euro per year) | 15,393 | 14,976 |
| flat tax rate | 0.204% | 0.198% |
| as % of EU budget | 10.92% | 10.62% |
| as % of EU GDP | 0.13% | 0.12% |
-
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes.
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.
Impact on child poverty in the EU.
| EU CBI scheme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 abs | 50ppp | |||
| A. poverty line fixed to the baseline at 60% of equivalised median disposable income | ||||
| Headcount rate | ||||
| Baseline (without EU CBI) | 17.0% | |||
| Reform (with EU CBI) | 14.6% | 14.9% | ||
| Difference in percentage points | −2.4 | −2.2 | ||
| Proportional reduction (%) | Poverty gap | 14.2 | 12.7 | |
| Baseline (without EU CBI) | 26.5% | |||
| Reform (with EU CBI) | 24.9% | 25.2% | ||
| Difference in percentage points | −1.6 | −1.1 | ||
| Proportional reduction (%) | 6.2 | 4.3 | ||
| B. poverty line fixed to the baseline at 40% of equivalised median disposable income | ||||
| Headcount rate | ||||
| Baseline (without EU CBI) | 5.4% | |||
| Reform (with EU CBI) | 4.3% | 4.5% | ||
| Difference in percentage points | −1.1 | −0.9 | ||
| Proportional reduction (%) | Poverty gap | 20.8 | 16.7 | |
| Baseline (without EU CBI) | 31.7% | |||
| Reform (with EU CBI) | 29.3% | 29.8% | ||
| Difference in percentage points | −2.4 | −2.1 | ||
| Proportional reduction (%) | 7.7 | 6.6 | ||
-
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes. Poverty indices are computed for the population of children under 6 years of age. The EU poverty rate is calculated by adding up the number of such children calculated to be below the national poverty thresholds in each country and dividing by the EU population of children in this age group.
-
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.
Impact on child poverty per country (children under 6 years of age).
| Baseline poverty rate (%) | Poverty rate after the reform (%) | Proportional reduction in poverty (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50abs | 50pps | 50abs | 50pps | ||
| Belgium | 12.2 | 10.0 | 9.8 | −18 | −20 |
| Bulgaria | 26.1 | 18.1 | 21.8 | −31 | −16 |
| Czech Republic | 9.6 | 7.2 | 7.6 | −25 | −21 |
| Denmark | 6.9 | 6.9 | 6.8 | 0 | −1 |
| Germany | 14.2 | 12.8 | 12.5 | −10 | −12 |
| Estonia | 13.7 | 9.9 | 10.9 | −27 | −20 |
| Ireland | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.0 | −7 | −7 |
| Greece | 20.4 | 18.1 | 18.5 | −12 | −10 |
| Spain | 17.0 | 15.5 | 15.5 | −9 | −9 |
| France | 16.6 | 15.4 | 15.0 | −7 | −9 |
| Italy | 20.2 | 18.4 | 18.4 | −9 | −9 |
| Cyprus | 13.1 | 9.9 | 9.9 | −25 | −25 |
| Latvia | 21.4 | 17.0 | 18.6 | −20 | −13 |
| Lithuania | 15.8 | 11.6 | 13.4 | −27 | −15 |
| Luxembourg | 9.4 | 7.5 | 7.2 | −20 | −23 |
| Hungary | 18.0 | 11.4 | 12.9 | −37 | −28 |
| Malta | 18.3 | 14.9 | 15.9 | −19 | −13 |
| Netherlands | 11.7 | 10.1 | 9.2 | −14 | −22 |
| Austria | 13.7 | 11.0 | 11.0 | −20 | −20 |
| Poland | 18.5 | 14.3 | 15.5 | −23 | −16 |
| Portugal | 15.1 | 11.7 | 12.9 | −23 | −15 |
| Romania | 26.2 | 16.9 | 21.3 | −35 | −19 |
| Slovenia | 11.1 | 9.4 | 9.5 | −15 | −15 |
| Slovakia | 13.8 | 9.6 | 11.2 | −30 | −19 |
| Finland | 12.4 | 10.7 | 10.2 | −14 | −18 |
| Sweden | 12.1 | 11.9 | 11.8 | −1 | −2 |
| United Kingdom | 19.7 | 17.3 | 17.3 | −12 | −12 |
-
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes. Poverty rate of children under 6 years of age. The poverty line defined as 60% of national equivalised median disposable income in the baseline.
-
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.
Impact on overall poverty per country.
| Baseline poverty rate (%) | Proportional reduction in overall poverty (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 50abs | 50pps | ||
| EU | 15.9 | −2 | −2 |
| Belgium | 11.6 | −2 | −2 |
| Bulgaria | 20.0 | −4 | −2 |
| Czech Republic | 7.9 | −2 | −1 |
| Denmark | 10.4 | 2 | 3 |
| Germany | 14.2 | −1 | −1 |
| Estonia | 15.6 | −3 | −3 |
| Ireland | 13.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Greece | 20.8 | 0 | 0 |
| Spain | 18.8 | −1 | −1 |
| France | 13.3 | −1 | −2 |
| Italy | 17.5 | −1 | −1 |
| Cyprus | 14.6 | −3 | −3 |
| Latvia | 20.1 | −1 | −1 |
| Lithuania | 17.8 | −1 | 0 |
| Luxembourg | 8.2 | −3 | −3 |
| Hungary | 11.3 | −8 | −7 |
| Malta | 16.1 | −2 | −1 |
| Netherlands | 10.2 | −2 | −3 |
| Austria | 11.8 | −3 | −2 |
| Poland | 17.5 | −2 | −1 |
| Portugal | 19.1 | −3 | −2 |
| Romania | 23.1 | −5 | −3 |
| Slovenia | 13.7 | −2 | −2 |
| Slovakia | 9.4 | −5 | −4 |
| Finland | 11.9 | −2 | −2 |
| Sweden | 12.4 | 1 | 1 |
| United Kingdom | 16.3 | −2 | −2 |
-
Notes: ‘50abs’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month. ‘50ppp’ is a Child Basic Income scheme that pays €50 per month adjusted for power purchasing parity. All children below the age of 6 in the EU would be eligible under both schemes. Poverty rate of total population. The poverty line defined as 60% of national equivalised median disposable income in the baseline.
-
Sources: Own calculations based on EUROMOD F5.36.

