Stay on Target: Population Projections and Microsimulation Design
Figures
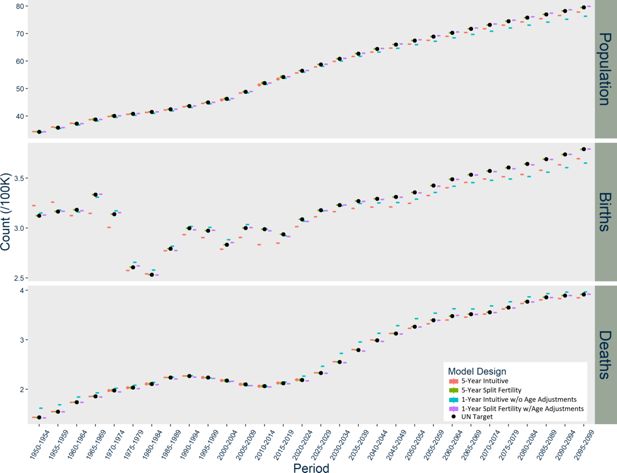
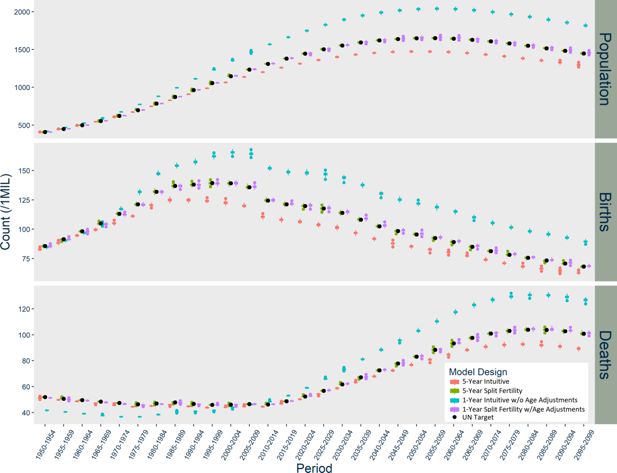
Results of Norway Models with Additional Stochasticity Options, scaled up to actual population size
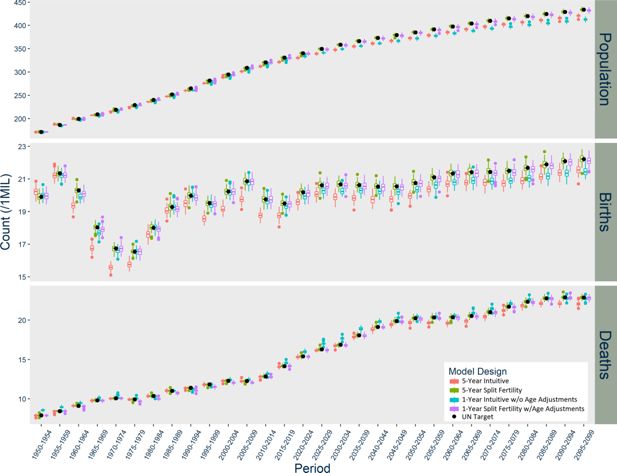
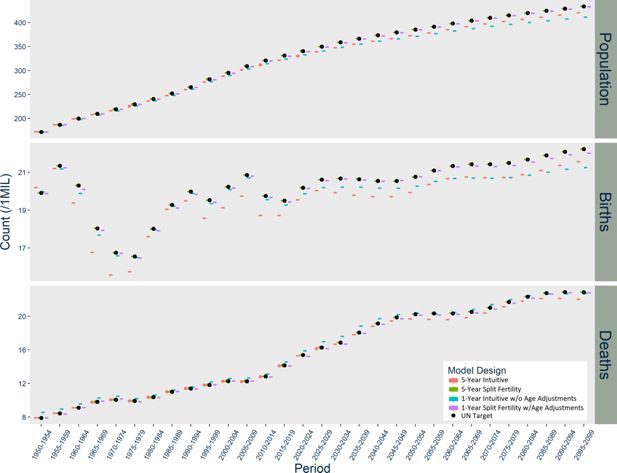
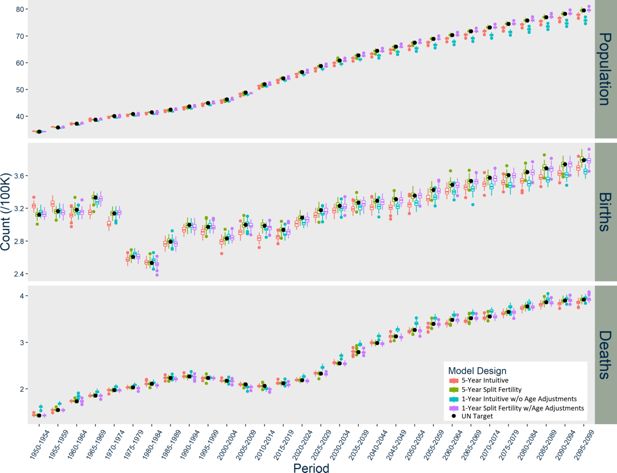
Results of USA Models with Additional Stochasticity Options, scaled up to actual population size
Tables
Assignment of Demographic Event Risk by Age for 1-year Split Fertility Design
| t=0 | Rnd. 2 | t=1 | Rnd. 2 | t=2 | Rnd. 2 | t=3 | Rnd. 2 | t=4 | Rnd. 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agent Age Characteristics | ||||||||||
| Current Age | 43 | 44 | 44 | 45 | 45 | 46 | 46 | 47 | 47 | 48 |
| Starting Age | 43 | 43 | 43 | 43 | 43 | |||||
| Ending Age | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | |||||
| Corresponding Age Labels for UN Statistics | ||||||||||
| Fertility Rate | 40-44 | 40-44 | 40-44 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 |
| Survival Ratio | 40-44 | 40-44 | 40-44 | 40-44 | 40-44 | |||||
| Migration Count | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | 45-49 | |||||
Years of Risk among Newborn Cohorts
| Cohort | Year 0 | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Total Years of Risk | Percent of Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 33 |
| B | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 27 | |
| C | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 20 | ||
| D | 1 | 1 | 2 | 13 | |||
| E | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||||
| Total | 15 | 100 |
Model Design Characteristics and Formulas
| Intuitive Models | Split Fertility Models | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | 5-year step and interval t =T= [1950,1955,…2100] | 1-year step t= [0,1,2,3,4], 5-year interval T=[1950,1955,…2100] | 5-year step and interval t =T= [1950,1955,…2100] | 1-year step t= (0,1,2,3,4), 5-year interval T=[1950,1955,…2100] |
| Event ordering | 0) Initialization, 1) fertility, 2) infant initialization, 3) mortality, 4) aging, 5) migration, 6) time step/interval advancement, T+5. | 0) Initialization, 1) fertility, 2) infant initialization, 3) mortality, 4) aging, 5) migration, 6) time step advancement, 7) repeat events 1-6 for t<5 until interval advancement, T+5. | 0) Initialization, 1) fertility (round one), 2) infant initialization (round one), 3) mortality, 4) aging, 5) migration 6) fertility round two, 7) infant initialization (round two), 8) second round infant mortality, 9) second round infant aging 10) time step/interval advancement, T+5. | 0) Initialization, 1) fertility (round one), 2) infant initialization (round one), 3) mortality, 4) aging, 5) migration 6) fertility round two, 7) infant initialization (round two), 8) second round infant mortality, 9) second round infant aging 10) time step advancement, 11) repeat events 1-10 for t<5 until interval advancement, T+5. |
| Current age (A) | 5-year age groups, A=[0,5…105] | 1-year age groups A=[0,1,…105] | 5-year age groups, A=[0,5…105] | 1-year age groups A=[0,1,…105] For immigrants: A=eA-t |
| Initial age (iA) | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | iA=A-t |
| End age (eA) | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | Not Applicable | eA=A+(5-t) |
| Model Age-Specific Fertility Rates (ASFR) | ; Apply to current age (A) | ; Apply to current age (A) | ||
| Infant initialization | Assigned age -5, and sex based on UN sex ratio | Assigned age -1, and sex based on UN sex ratio | Assigned age -5, and sex based on UN sex ratio | Assigned age -1, and sex based on UN sex ratio. |
| Model Mortality Rate (MR) | 1 - (UNSR) | ; Apply to current age (A) | 1 - (UNSR) | ; Apply to initial age (iA). For newborn cohorts: ; For agents age 110+: 1. For immigrants: no mortality |
| Model Emigration count (EC) | (UNEC) * (Sample%) | ; Apply to current age (A) | (UNEC) * (Sample%) | ; Apply to end age (eA). For newborn cohorts: |
| Model Immigration count (IC) | (UNIC) * (Sample%) | ; Apply to current age (A) | (UNIC) * (Sample%) | ; Apply to end age (eA). For newborn cohorts: Note: All immigrants receive a tag to provide immunity to mortality and emigration. |
| Immigrant initialization | Assign current age (A) | Assign current age (A) | Assign current age (A) | Assign end age (eA), then calculate A and iA by subtracting remaining time steps and 5, respectively. |
| Period advance | NA | t + 1 | NA | t + 1 |
| Interval advance | T + 5, remove any tags that identify newborn cohorts or immigrant agents | |||
Average Percent Divergence from UN Target Values in 5-year Models
| Births | Deaths | Total Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Period | Intuitive | SF* | Intuitive | SF* | Intuitive | SF* |
| Norway | 1950-2099 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 0.8 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 |
| 1950-1999 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | |
| 2000-2049 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | |
| 2050-2099 | 2.7 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | |
| USA | 1950-2099 | 3.7 | 0.0 | 1.8 | 0.0 | 2.7 | 0.0 |
| 1950-1999 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 1.3 | 0.0 | |
| 2000-2049 | 4.2 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | |
| 2050-2099 | 3.4 | 0.0 | 3.1 | 0.0 | 3.2 | 0.0 | |
| India | 1950-2099 | 9.3 | 0.0 | 7.0 | 0.0 | 8.9 | 0.0 |
| 1950-1999 | 7.3 | 0.0 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 4.0 | 0.0 | |
| 2000-2049 | 11.2 | 0.0 | 5.0 | 0.0 | 9.3 | 0.0 | |
| 2050-2099 | 9.4 | 0.0 | 10.1 | 0.0 | 10.7 | 0.0 | |
-
*
Split Fertility Design
Average Percent Divergence from UN Target Values in 1-year Models
| Births | Deaths | Total Population | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Period | Intuitive | SF* | Intuitive | SF* | Intuitive | SF* |
| Norway | 1950-2099 | 1.6 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 0.3 |
| 1950-1999 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 0.1 | |
| 2000-2049 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 1.3 | 0.2 | |
| 2050-2099 | 2.9 | 0.1 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 0.4 | |
| USA | 1950-2099 | 2.0 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 3.1 | 0.3 |
| 1950-1999 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 3.6 | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.2 | |
| 2000-2049 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 0.6 | 2.7 | 0.3 | |
| 2050-2099 | 3.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 0.2 | |
| India | 1950-2099 | 19.5 | 0.3 | 20.8 | 0.6 | 20.7 | 0.3 |
| 1950-1999 | 8.1 | 0.3 | 18.3 | 1.1 | 11.1 | 0.3 | |
| 2000-2049 | 23.8 | 0.4 | 14.6 | 0.5 | 21.2 | 0.3 | |
| 2050-2099 | 29.4 | 0.3 | 25.7 | 0.4 | 24.4 | 0.4 | |
-
*
Split Fertility Design
Data and code availability
The authors used publicly available data for this analysis. The 2019 Revision of the World Population Prospects are available as excel files to download from the archive section of the United Nations website: https://population.un.org/wpp/Download/Archive/Standard/. The data are available without registration and are not proprietary.
The model was built in AnyLogic version 8.7.6. AnyLogic can be downloaded and installed at: https://www.anylogic.com/downloads/. There is a free personal learning edition that can load the model and run the model at low agent counts. An AnyLogic Professional or Researcher license is required to run the model at the scale ran in the paper (100K initial agents).
Results from the AnyLogic models were compiled and made into graphs using R version 4.1.2. R is open-source and can be downloaded and installed at: https://www.r-project.org/.
The AnyLogic and R code for this paper are available as replication materials on a GitHub repository accessible at: https://github.com/centerformindandculture/UN-CCM-2-MICROSIM. Others can re-use the code under a Creative Commons license, and we request our paper be cited when borrowing portions of the code.